Background: Stroke is a known complication of Continuous Flow Left Ventricular Assist Devices (CF-LVAD). Patients supported by CF-LVAD such as the HMII, HM3 and HVAD are prescribed warfarin and anti-platelet agents to prevent thrombus formation in the pump. Despite improvements in LVAD technology, stroke related morbidity and mortality remains substantial.
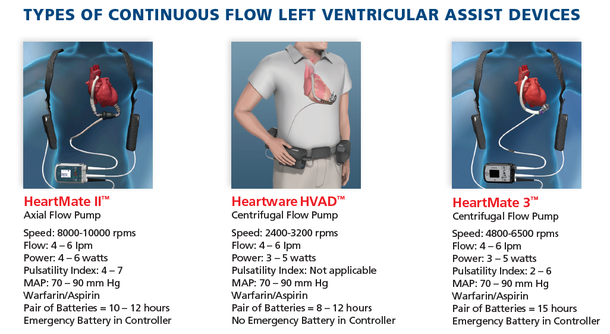
Objective: Provide guidance for clinicians when caring for an LVAD patient with suspected stroke in the community or on the URMC campus.
Triage Guideline for VAD Pt at Outlying Center with Suspected Stroke Copy Link
Community LVAD patients are directed to seek treatment in their local ED for any sign/symptom of stroke. Upon arrival to the ED patient will require:
- Stat labs including CBC, INR, CMP, LDH
-
Non-contrast head CT and head and neck CT angiogram if center is able to perform CT
angiogram (Request CT imaging be uploaded to Nuance® PowerShare or eView as
appropriate)
- If CT indicates a hemorrhage, Reverse to an INR ≤ 1.3 with 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (Kcentra). Administer Kcentra 1000 units or consider 15 units/kg (up to 1500 units) AND Vitamin K 10 mg IV once. Re-check INR 30 minutes after administration. If INR has not reached goal, may give additional 500 units of Kcentra IV.
-
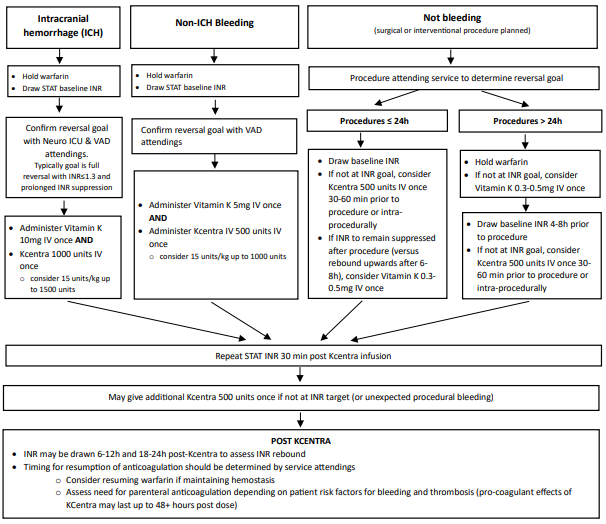
- For patients with an INR result within 72 hrs of presentation , dose Kcentra based on that INR.
- For centers that do not have Kcentra, discuss with them their protocol for emergent warfarin reversal.
- Instruct outlying facility to call the transfer center 800-499-9298
- Transfer center will alert Endovascular Neurosurgery Attending, VAD Cardiology attending, and Neuromedicine ICU attending and collaborate on transfer to SMH for further management including LVAD interrogation and possible head/neck CT angiogram.
- Blood pressure goal MAP 80-90
-
If no hemorrhage, Transfer Center will alert Stroke Team and
VAD Cardiology Attending and collaborate on transfer to SMH. A head and neck CT angiogram
will be done at SMH if not done at the outside center. Patients will be admitted to the
Neuromedicine ICU.
- Blood Pressure Goal: MAP 80-100
- Typically, LVAD patients would not be candidates for thrombolysis as they are usually on warfarin. If no recent bleed and not on warfarin, thrombolysis may be a consideration. Consult UR guideline: Emergency Evaluation and Management of Adult patient with Suspected Ischemic Stroke
Inpatient Guideline Copy Link
Surgical Planning (including Digital Subtraction Angiography) Copy Link
- Notify OR scheduler patient has an LVAD and requires perfusionist and cardiac anesthesia for all cases
- Elective cases: Schedule M-F prior to 11am to ensure perfusionist available
- Emergent Cases: in addition to alerting OR desk at time of booking, page perfusion on call
Guideline for Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage Copy Link
- Reverse to an INR ≤ 1.3 with 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (Kcentra). Administer Kcentra 1000 units or consider 15 units/kg (up to 1500 units) AND Vitamin K 10 mg IV once. Re-check INR 30 minutes after administration. If INR has not reached goal, may give additional 500 units of Kcentra IV.
-
Follow Warfarin Reversal for VAD with ICH:
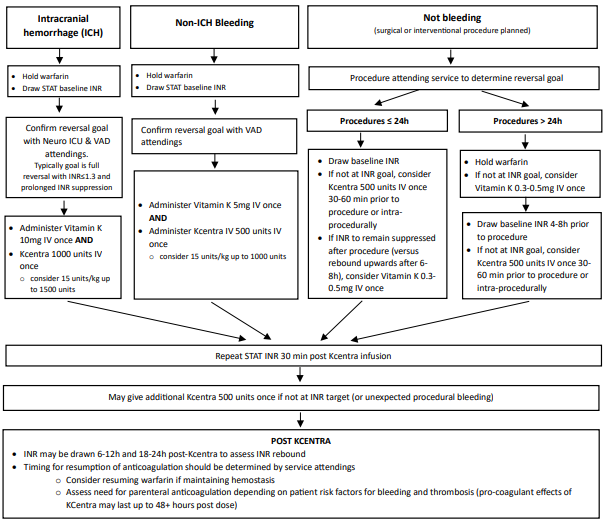
- Nursing Care: LVAD patients may only be admitted to VAD trained units: 4-1600, 4-2800, 4-3400, 4-3600 or 8-1200.
- Imaging: Repeat scan typically after 6 hours (sometimes sooner).
- BP goals: MAP goal 80-90.
- Resumption of anti-coagulation: Timing will be determined by the Stroke/Neurosurgery Attending in collaboration with VAD Cardiology Attending (If no intervention is done, Stroke team will lead management, if intervention done, then Neurosurgery will lead management). If the decision is made to resume anticoagulation, would recommend starting Neuro protocol Heparin without a bolus. Head CT will be obtained 24 hours post achieving therapeutic PTT on heparin. If no evidence of further bleeding, then would start warfarin. If there is a need for procedures can continue IV heparin or enoxaparin. For HM 3 patients can consider not continuing heparin when starting warfarin (Neuro protocol heparin is used initially as a test to assess if patient will bleed).
- Resumption of anti-platelets: Aspirin 81 timing varies, discuss with Neurology/Neurosurgery and VAD Cardiology attending.
- Follow-up: Patient will follow-up with Neurosurgery or Neurology as appropriate.
Guideline for Suspected Acute Ischemic Stroke Copy Link
Refer to the following UR guidelines; Neuroendovascular Intervention for Acute Ischemic Stroke in Adults , Management of Adults with Ischemic Stroke and TIA , and Emergency Evaluation and Management of Adult Patient with Suspected Ischemic Stroke
- Imaging: Non-contrast head CT and head and neck CT angiogram for initial imaging. Follow-up imaging based on case. If thrombectomy, f/u CT scan per Neurosurgery, typically within 12 -24 hours. If thrombolysis done, scan 24 hours post thrombolysis.
-
BP goal: Permissive hypertension for a few days:
Thrombectomy: MAP goal 80-90 mm Hg (Non contrast head CT 12 to 24 hours post thrombectomy). Can liberalize blood pressure goal after follow-up CT. Discuss blood pressure goal with Endovascular Neurosurgeon.
No Thrombectomy: MAP goal 80-100 mm Hg. - Anticoagulation- Dependent on size of stroke and hemorrhagic transformation and need for hemicraniectomy.
- Antiplatelet dosing: Typically before end of Hospital Day 2. Discuss timing of antiplatelet therapy with Endovascular Neurosurgeon. Start DVT Prophylaxis by end of Hospital Day 2.
References Copy Link
Willey, J., Colombo, P., Lazar, R. et al. JHLT 2014;33:878-887
Statement Copy Link
Guidelines are intended to be flexible. They serve as reference points or recommendations, not rigid criteria. Guidelines should be followed in most cases, but there is an understanding that, depending on the patient, the setting, the circumstances, or other factors, guidelines can and should be tailored to fit individual needs.